
"The history of blood pressure measurement," J Hum Hypertens 8(2):73-84, 1994.
KOROTKOFF SOUNDS PROFESSIONAL
"Recommendation for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement of professionals from the subcommittee of professional and public education of the American heart association council on high blood pressure research," Hypertension.

"2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension," Eur Heart J, 34: 2159-2219, 2013.
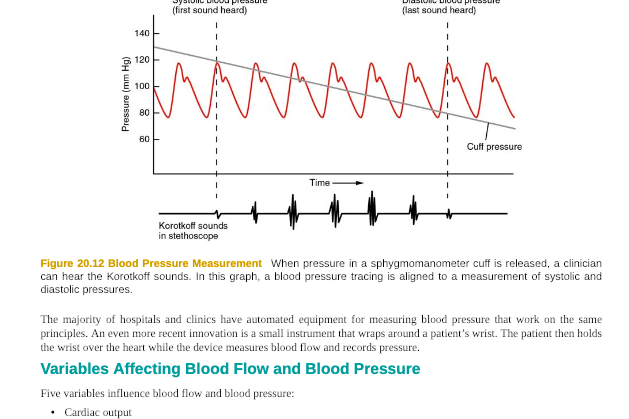
Developed device including sensor implemented inside the cuffįigure 5. Pulse waves before cuff inflation and without a signal filterįigure 4. Sensing module (left) and schematic diagram of sensing module (right)įigure 2. Blood pressure measurements based on Korotkoff sound signals obtained by using the developed PVDF film-based sensor module are accurate and highly correlated with measurements obtained by the traditional auscultatory method.įigure 1. Correlation coefficients for the values obtained by the auscultatory method and from the developed device were 0.982 and 0.980 for systolic and diastolic blood pressure, respectively. The results from 86 out of 90 systolic measurements and 84 out of 90 diastolic measurements indicate that the developed device pass the validation criteria of the international protocol. An algorithm for determining starting and ending points of the Korotkoff sounds was established, and clinical data from subjects were acquired and analyzed to find the relationship between the values obtained by the auscultatory method and from the developed device. PVDF-based sensor pattern was developed to function as a vibration sensor to detect of Korotkoff sounds, and the film's output was connected to an impedance-matching circuit. In this study, we develop a Korotkoff sound based automatic blood pressure measurement device including sensor, hardware, and analysis algorithm.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
